Evaluation of animal welfare.
Animal Welfare Efforts
At Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium, to properly rear rare species such as whale sharks, large elasmobranchs, and dolphins, we conduct assessments for each reared animal based on five factors (nutrition, environment, health, behavior, psychology) recommended by WAZA (World Association of Zoos and Aquariums) and JAZA (Japanese Association of Zoos and Aquariums).
| Index | |
| What is animal welfare? | About the assessment system |
| April 2021-March 2022 | April 2020-March 2021 |
| April 2019-March 2020 | |
What is animal welfare?
Animal welfare is efforts toward animal well-being and quality of life (QOL). Our goal is increasing the animals' opportunities for comfort, pleasure, interest, and satisfaction as well as creating a breeding environment, including food, breeding facilities, animal health and safety.
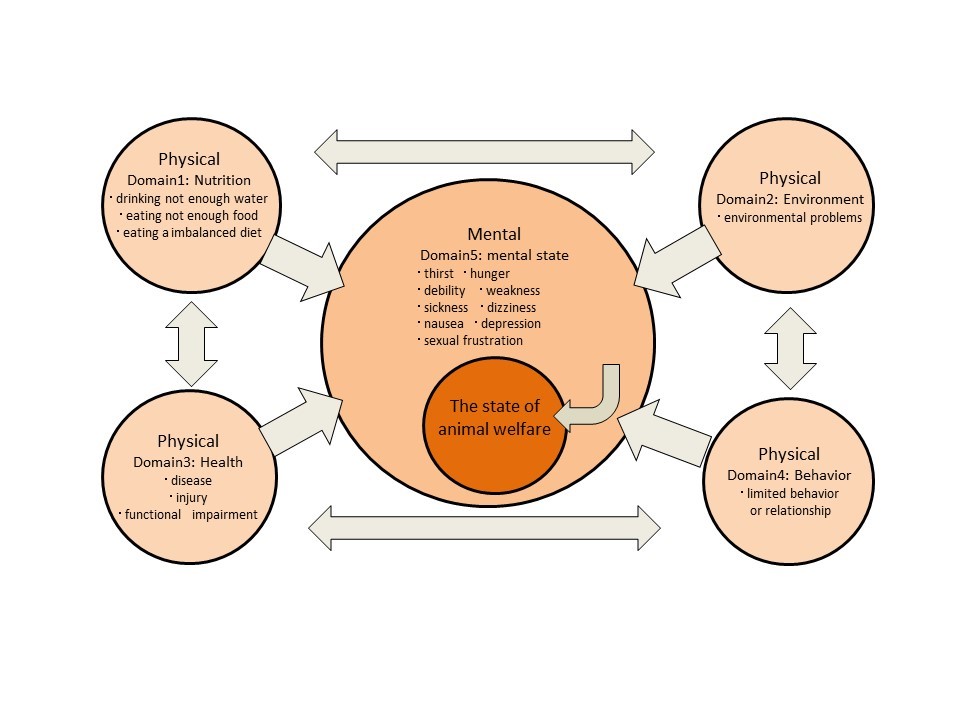
Mellow et al. 2009: Mellow 2013.
The welfare of reared animals is influenced by four physical factors (nutrition, environment, health, behavior) and one psychological factor (mental condition).
Evaluating these five factors will help to improve animal welfare.
About the assessment system
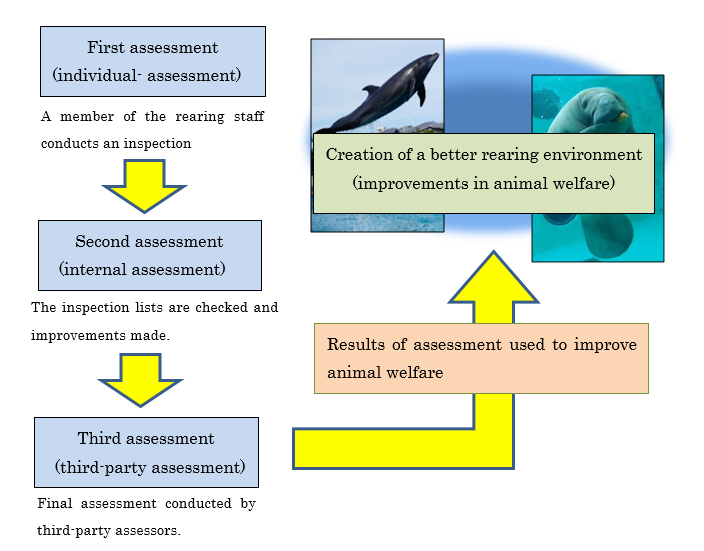
First assessment (individual- assessment)
Individual-assessments have 108 checks grouped into five areas.
A member of the rearing staff conducts the first assessment.

A member of the rearing staff conducts an inspection
Second assessment (internal assessment)
Assessment charts for the primary assessments are checked to further improve animal welfare.
Secondary assessments are usually conducted by the veterinarian or the head of each rearing section.
Third assessment (third-party assessment)
The final assessment is an inspection of the rearing site by third-party assessors (over 2 people) who have attended lectures in animal welfare through JAZA. The results of the final assessments are given to the staff so that improvements can be made to the rearing environment for the animals.

Final assessment conducted by third-party assessors.
Activity report
April 2021-March 2022
Activity content
- March 7th, 2022:Third assessment conducted
※To prevent the spread of covid-19, assessment sheets sent by e-mail.
January 7th, 2022:Second assessment conducted
December 15th, 2022:First assessment conducted
Examples of improvements
Stable rearing implemented for giant manta
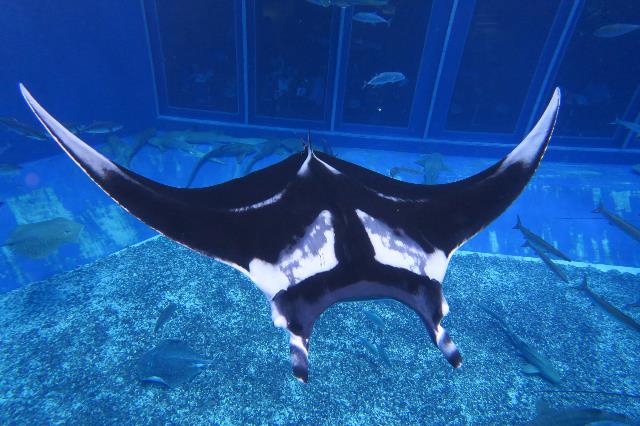

The ecology of giant mantas is mostly unknown, as they had never been reared in Japan or overseas. During the world’s first successful exhibit at our facility in 2018, we were able to observe its behavior, and conduct blood tests and ultrasounds to better understand giant manta physiology and ecology. We noticed unusual behavior such as unstable swimming and feeding during the colder months. By adjusting the food given in colder months, and reducing interference from other animals, the problematic behavior stopped, creating a good environment all year.
Third-party assessors
Koichi Murata:Yokohama Zoo Zoorasia DirectorNaoki Kamezaki:Okayama University of Science of Professor
Suma Aqualife Park KOBE Former Director
April 2020-March 2021
Activity content
- March 17th, 2021:Third assessment conducted
※To prevent the spread of covid-19, assessment sheets sent by e-mail. - December 18th, 2020:Second assessment conducted
- October 15-31th, 2020:First assessment conducted
Examples of improvements
The installation of a water temperature adjusting system in the Kuroshio Sea tank

In recent years, we have learned that wild whale sharks swim up and down between warm surface waters and cold deep-sea waters to adjust their body temperature. As global sea temperatures rise, Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium has installed a water temperature adjusting system, so whale sharks are better able to regulate body temperature, in this improved living environment.
Studies of thermoregulation of whale sharks can be viewed here.
Using toys to reduce aggressive behaviors in pygmy killer whales

Pygmy killer whales in the wild can be aggressive toward other dolphins. Aquarium staff had observed these aggressive behaviors toward other dolphins, while social behaviors such as swimming and playing together were limited. At Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium, efforts were made to control aggressive behavior using behavior modification methods (equivalent to psychotherapy in humans), to encourage social behavior with other dolphins. By repeatedly rewarding dolphins who didn’t show aggressive behaviors with toys, it reduced aggression, and increased socialization.
Research studies related to controlling aggressive behaviors in pygmy killer whales can be viewed here.
Third-party assessors
Koichi Murata:Yokohama Zoo Zoorasia DirectorNaoki Kamezaki:Okayama University of Science of Professor
Suma Aqualife Park KOBE Former Director
April 2019-March 2020
Activity content
- March 4th, 2020:Third assessment conducted
- December 20th, 2019:Second assessment conducted
- October 15-30th, 2019:First assessment conducted
Examples of improvements
Controlling frequent fighting between hawksbill turtles

Aggressive behaviors occur when rearing several hawksbill turtles in the same tank. To reduce aggressive behaviors of hawksbill turtles and create a comfortable environment, Okinawa Churaumi Aquarium studied variations in rearing environments while monitoring blood corticosterone concentration, a stress indicator in sea turtles. The results showed that adding chunks of limestone or rocks in the tank reduces turtle stress and decreases aggressive behaviors. The sea turtle pool now includes chunks of limestone, and aggressive behaviors between hawksbill turtles is rarely seen.
Research studies on reducing aggressive behaviors in hawksbill turtles can be viewed here.
Third-party assessors
Koichi Murata:Yokohama Zoo Zoorasia DirectorNaoki Kamezaki:Okayama University of Science of Professor
Suma Aqualife Park KOBE Former Director

